

To achieve this, external ‘work’ has to be applied using electricity. Heat pumps compress the cold outdoor air, thereby heating it to a warmer temperature and transferring it indoors without going against the energy conservation principle of the first law. A heat pump’s capacity to heat an indoor space is one of the applications of the Second Law of Thermodynamics. The Second Law of Thermodynamics asserts that material at a lower temperature will always be at the receiving end of heat from a material at a higher temperature. Heat pumps demonstrate the First Law of Thermodynamics by converting mechanical energy to thermal energy. In other words, energy is always conserved and remains constant. The First Law of Thermodynamics simply states that it is possible to for energy to change forms, but it cannot be created or destroyed. With these temperature scales, the properties of temperature are then labelled according to where they fall on the scale, for example, “hot” and “cold”. This law is very important because it enables us to define what we commonly know to be a scale of temperatures – and we can measure temperatures of any object we want with thermometers. The law states that if two systems A and B are in thermal equilibrium with each other, and systems B and C are also in equilibrium with each other, then systems A and C are in thermal equilibrium (in other words, the same temperature) with each other as well. The Zeroth Law of thermodynamics concerns temperature. The laws of thermodynamics explain how energy changes in a system and how the system can carry out useful work on its environment. The Laws of Thermodynamics and how They Apply to Heat Pumps The key factor here is that heat is a form of energy that is neither destroyed nor created, simply moved.
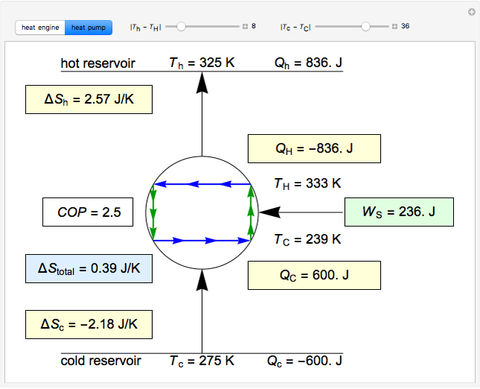
Very basically, the study of thermodynamics concerns how heat is transformed from one form to another and how it is transferred from one place to another. Thermodynamics is the science of the relationship between heat, work, temperature, and energy. In this article, we will explore how heat pumps work on the basis of thermodynamic principles. Whether you’re driving a car, enjoying the warmth of your heating system in your bedroom, or drinking a glass of chilled wine, you’re experiencing the results of thermodynamics in action. Thermodynamics is an intrinsic part of our daily lives. 3 - The Laws of Thermodynamics and how They Apply to Heat Pumps.2 - What is the Meaning of Thermodynamics?.1 - Heat Pumps’ Thermodynamics Information.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
